Stats Watch! 4
You knew that eventually we were going to come back to debunking some of the poor science claimed as “statistics” in the debate over homosexuality didn’t you? Here goes…
There is a report up on LifeSite News that claims that research in Australia looking at mental health figures for self-identified male and female homosexuals. LifeSite comments,
The study’s causal conclusions are challenged by other research showing the same high levels of mental health problems among homosexuals in countries where homosexuality has been normalized as in countries where it is scorned.
A study by Drs. Paul and Kirk Cameron of the Family Research Institute in 2007 revealed that there is no difference in homosexual health risk depending on the level of tolerance in a particular environment.
The researchers found that homosexuals in the United States and Denmark – the latter of which is acknowledged to be highly tolerant of homosexuality – both die on average in their early 50’s, or in their 40’s if AIDS is the cause of death. The average age of death for all residents in either country ranges from the mid-to-upper-70s.
Lets look at these claims, that research shows high levels of mental health problems amongst homosexuals in countries where there is much greater tolerance and acceptance (which would debunk the idea that gay mental health issues are mainly to do with discrimination and intolerance). The paper cited to support this is this piece by Paul Cameron.
This paper is a poor piece of research. Let me say that again. It is poor. In order to build their database Cameron et al did two things. For the USA figures they went through the obituaries section of a famous gay newspaper and compared them to a secular newspaper. This means that this was not a random sample controlled for population, but rather a biased sample (biased in this sense towards the people whose obituaries were reported). All this data tells us is the different mean age at death between the these two samples – it does NOT tell us anything about the wider “gay” and “straight” populations unless we have a method of resampling to extrapolate to these wider populations. Such a method is not provided.
The Norwegian and Danish figures are more interesting because they come from official government statistics. The claim is that the official figures show a mean age at death for men in a gay union of 20 years lower then those in a heterosexual union. However, as the original researchers noted at the time, the first cohort of married gay men (i.e. those who entered into marriage immediately after the law changed) included a large number of people with terminal illnesses.
Authors from the Family Research Institute, a US-based institution ï¬ghting to ‘‘restore a world . . . where homosexuality is not taught and accepted, but instead is discouraged and rejected at every level,’’ have produced a series of reports in which they claim homosexuality is incompatible with full health and as dangerous to public health as drug abuse, prostitution, and smoking.
In a recent report, the authors obtained data from Statistics Denmark and Statistics Norway and compared the average age at death among men and women who had ever been in a same-sex marriage with the average age at death among people who had ever been heterosexually married. Because the age distribution among persons in same-sex marriages was considerably younger than that of people who had ever been heterosexually married, the average age at death among those who actually died during the observation period was, not surprisingly, considerably younger in the population of samesex married persons. The Family Research Institute presented the lower mean age at death (by 22–25 years) for persons in same-sex versus heterosexual marriages as evidence that persons who married heterosexually ‘‘outlived gays and lesbians by more than 20 years on average.’’
Elementary textbooks in epidemiology warn against such undue comparisons between group averages because they lead to seemingly common-sense yet seriously flawed conclusions.
Does that make sense? The average age of those entering a gay marriage was much younger then those entering a heterosexual marriage. This meant that in the limited time period of observation, if any of the gay men died they would be, on average, much younger then the “straight” cohort. The proper way to do this kind of research would be to normalise for age first, i.e. what you want to do is to compare to men aged the same (let’s say 35) who enter at the same time into a gay and straight marriage respectively and then see if there are differences in outcomes.
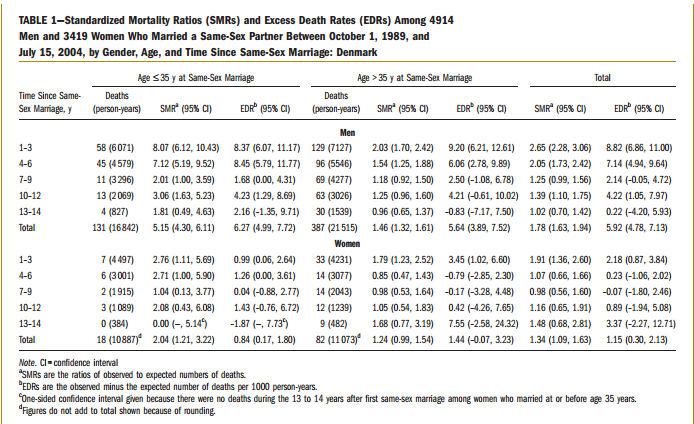
The original research does try to do this by looking at longer term outcomes. By removing the first year’s deaths (i.e. those people who entered a gay marriage and died within the first year – indicating that they were knowingly terminally ill at marriage), the dramatic figure of “Die 20 years younger” falls away. Here’s the table from the research.
Here’s how to read the table. The “SMR” value is the ratio of observed to expected number of deaths. For example, if the value is 2 then the death rate is twice as high as expected in the general population. The “EDR” value is a measure of the change in average age of death (so an EDR of 5 would indicate that on average, people in this group die 5 years younger then expected).
You can see straight away that the “20 years younger” figure is fallacious. The 1-3 years of gay marriage group has overall an EDR of 8.82, indicating that this group dies on average 9 years earlier then expected. By the time you get further down the table you start to get EDRs that are negligible. But there’s more to the table, because we also have the 95% confidence interval bands. These are the range of values within which we’re 95% confident that the real figure actually lies (because we’re dealing with samples of the population). Look at the EDR values – the 7-9 and 13-14 groups have an lower bound of below 0, indicating that we are not certain whether the average age at death might actually be higher then the “straight” comparison population.
The overall figure for EDR is 5.92 (so married gay men die on average 6 years before their straight counterparts). That’s not great, but it’s nowhere near the sensationalist 20 years figure put out by Cameron. But there’s more! The researchers looked at those gay men who married after the mid 90s (when HIV treatment became much more effective) and found that for this population the mortality rates were much more improved. As the abstract reports,
Mortality was markedly increased in the ï¬rst decade after same-sex marriage for men who married between 1989 and 1995 (SMR= 2.25; 95% conï¬dence interval [CI] = 2.01, 2.50), but much less so for men who married after 1995, when efï¬cient HIV/AIDS therapies were available (SMR= 1.33; 95% CI=1.04, 1.68). For women who married their same-sex partner between 1989 and 2004, mortality was 34% higher than was mortality in the general female population (SMR=1.34; 95% CI=1.09, 1.63). For women, and for men marrying after 1995, the signiï¬cant excess mortality was limited to the period 1 to 3 years after the marriage.
Yes, still slightly worse then the heterosexually partnered population, but nothing in the region of the “20 years shorter lifespan” figure cited by Cameron et al.
Stats Watch Ranking
2 out of 5
It’s not that the basic thesis (married gay men have a shorter lifespan then married straight men) is incorrect, it’s just that there are obvious reasons why the first tranche of married gay men in Denmark and Norway had remarkably short lifespans. Once you take this abnormal group out of the dataset (and once you deal with data from after the improvements in HIV care in the 90s), the figures become much more similar to heterosexual married men and certainly nothing like the “die 20 years younger” nonsense bandied around.
What the quoting of these figures by LifeSite and others also demonstrates is a basic lack of awareness of key statistical concepts around confidence intervals. The figures for gay men married for more than 6 years are approaching statistical insignificance, indicating that the real driving factor behind the mortality differences that we do see is less to do with homosexuality per se and more to do with the types of men who entered gay marriages in Denmark and Norway in their early years.
Although there is some basis for making the claim that gay men die younger then straight men, it behoves those who would seek to make such a claim to be honest with the evidence available and to point out the areas (i.e. gay men married for more than 6 years) where there is no difference with straight counterparts.
How about doing some research on this kind of thing, for a change?
http://www.europeandignitywatch.org/day-to-day/detail/article/eu-fundamental-rights-agency-fabricates-victims-of-lgbt-discrimination-in-a-new-survey.html
What kind of “research” do you propose?
And do you accept that the “die 20 years younger” claim is a gross mis-statement by Cameron et al?
The kind of research which you have in mind, Jill, is presumably the same kind of research that ought to be done on this kind of thing:
http://www.pinknews.co.uk/2012/04/08/analysis-why-the-c4m-petition-is-flawed-and-untruthful/Â
That’s an interesting piece Will. Let me make some brief comments.
The objection to the C4M petition is fourfold. First, it is on the basis of who is behind it. I think you’ll agree this is ad hominem. Second, there is the claim that the vertical jumps are paper-based petitions and there is doubt as to whether such numbers of paper petitions were received. No evidence is presented to support this conjecture. Third, there is a claim made about online petition numbers versus web hits, but no actual numbers are presented. It isn’t clear what this “NetStat” system is, but it certainly won’t be the actual hard numbers of visitors to the site. No evidence is provided to support this claim.
Where the piece has valid criticism is that there is no validation of email addresses used to sign the petition and neither is there any attempt to prevent non UK residents signing. The second is harder to prevent then the first, given that many “UK” ISPs actually operate from the EU. However, I am led to believe that the C4M campaign does attempt to do some preliminary scrutiny of e-signatures and some are removed when there is doubt about their heritage.
However, no evidence is presented that any major fraud of this type has occurred.
So we have three claims, one of which is just ad hominem and the others for which no actual evidence is presented. The areas where there might be some concern, once again no evidence is presented that any major issues in these areas has arisen.
As I commented on your other piece, it’s a case of blaming the messenger.
Catholic Voices have Pink News’s measure, Will.
http://www.catholicvoices.org.uk/monitor-blog/2012/04/pink-news-smear-debases-debate
Jill, the argument seems to hinge on the way the questions are proposed. As the article you post says in criticism of the way the other two polls posed their questions – those that found higher levels of support rather than the 70% their poll found: “None of these polls, however, made clear that introducing gay marriage involves redefining marriage. The point they raise is interesting but is it accurate? It also raise the question whether that was the tipping point that made people vote the way they did. So it comes down to two things:
1. Is it true that the opening up of civil marriage to gay people is going to fundamentally redefine marriage?
2. Would making it plain ON THE SURVEY that marriage will be redefined by the government’s proposal cause such a huge discrepancy in survey results?
I’d like to know what you, Jill, and others think about both questions, but in the meantime I’ll put in my ha’pence worth.
1. I am not at all sure opening marriage up amounts to a redefinition. Has marriage been redefined in countries where same-sex marriage is legal or is recognised if conducted abroad? Have the following countries really redefined marriage for everyone else – Argentina, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Iceland, Israel, Mexico, The Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, South Africa, Spain, Sweden and some states in the United States?
2. Even if it were true that marriage would be redefined is this necessarily a bad thing? When married women gained rights over their property in 1882 I am sure men at the time might have thought this was a “redefinition of marriage that badly affected them”. Even so, I would contend if it could be called a redefinition it was a redefinition for the common good. The same could be claimed for opening up CIVIL marriage to gay people.
One last thing, I am sure Peter would agree, the way the questions are asked should be as bland as possible with no scare-tactics pointing to the answers you want. If, for example, you were to ask people if they agree that marriage as we know it should be completely redefined of course you are going to get a NO vote.
Just to briefly respond to your two points Tom.
1 – The Government’s proposals amount to redefining marriage as
Civil Partnership. This is the effect of having to remove references
to sex, procreation and consummation. On that basis my marriage and
Jill’s marriage and everybody’s marriage has been redefined.
2 – The discrepancy does seem to occur for exactly this reason.
ComRes is a *highly* reputable polling firm that I have worked with
in the past. The questions were asked in a specific manner to
highlight this issue – once people have it explained to them what
the effect of gender-neutral marriage is (the removal of references
to sex and biological parenting), the numbers opposed alter
radically.
As for whether this redefinition is a good thing, well that’s for
the advocates of such a change to argue for (and for those of us who
are opposed to find reasonable ways to argue against).
I don’t think the ComRes questions were asked with any sense of
“scare tactics”. If anyone wants to suggest otherwise, perhaps they
could point to the actual wording that is scare-mongering?
 Yes, I think this is the case.
Peter will remember that this was the proposal around the time Civil Partnerships were first debated – back with the original Bill drafted by Lord Lester, although the thinking is decades older than this.
Then, Civil Partnership – as eventually defined for gay people only by the government Act – was intended as a forerunner of the new “gold standard” and I was led to believe before CPs came into being that there was a powerful head of steam to see the state withdraw from the marriage stakes altogether. As soon as the Bill passed this evaporated (or was it all my imagination?).
I think this proposed Bill came about because it proved too difficult for the State to “get out of marriage” and so the decision was to make what it offered as marriage more akin to what we have in Civil Partnerships.
Personally I have few probs with this. I think it is recognising what has already come about and will – I hope – give religious groups a wonderful opportunity to teach how different our model of marriage is to that embraced by the majority.
Our model being “exclusively male and female” as opposed to “any two people”?
Sorry, couldn’t resist…
 Naughty boy!
No supper for you!!
Very interesting, Martin. I recently went to a family wedding at one of the those Tudor mansions. The bride’s grandmother said to me after the ceremony, “Well, I wouldn’t feel married after that”. I added, “Well it was rather like a Civil Partnership”.
 I think that perception is precisely right.
I am presently trying to negotiate becoming a civil partnership registrar, the hostility from within the Registration Service is amazing!
Why should they be hostile?
Tell more.
Just to briefly respond to your two points Tom.
1 – The Government’s proposals amount to redefining marriage as Civil Partnership. This is the effect of having to remove references to sex, procreation and consummation. On that basis my marriage and Jill’s marriage and everybody’s marriage has been redefined.
2 – The discrepancy does seem to occur for exactly this reason. ComRes is a *highly* reputable polling firm that I have worked with in the past. The questions were asked in a specific manner to highlight this issue – once people have it explained to them what the effect of gender-neutral marriage is (the removal of references to sex and biological parenting), the numbers opposed alter radically.
As for whether this redefinition is a good thing, well that’s for the advocates of such a change to argue for (and for those of us who are opposed to find reasonable ways to argue against).
I don’t think the ComRes questions were asked with any sense of “scare tactics”. If anyone wants to suggest otherwise, perhaps they could point to the actual wording that is scare-mongering?
Peter, thank you for doing this. It is well known that such statistics are spurious because of the poor, incorrect or deliberately biased research on which they are based. You and I disagree about many things but I applaud you for this clarity. Thanks again. Happy Easter.
 But also “Yes!” – as it stands, precisely that.